faumachine is a virtual machine, similar in many respects to vmware[tm], qemu or virtual pc[tm]. what distinguishes faumachine from these other virtual machines, are the following features:
the faumachine virtual machine runs as a normal user process (no root privileges or kernel modules needed) on top of (currently) linux on i386 and amd64 hardware. the port of faumachine to openbsd and mac os x (intel) is in progress.
fault injection capability for experimentation in faumachine.
vhdl interpreter for automating experiments and tests based upon our project fauhdlc. we also ship example scripts for our vhdl interpreter that allow the automatic installation of several linux distributions and other operating systems using the distribution's cdrom.
the cpu of faumachine is based on the virtual cpu from fabrice bellard's excellent qemu simulator, which can execute anything a real x86/amd64 cpu can execute, too.
faumachine simulates a large variety of different hardware components, including
several x86 and amd64 cpus, ide and scsi controllers, ne2000 and intel eepro100 network interface adapters, an sb16 sound card, a generic vga and a cirrus gd5446 graphics adapter, a 24 and a 48 pin directi/o pcicard,
but also peripherals such as
networking hubs and routers, serial terminals, modems, a usbtoserial adapter, and even a threestory elevator.
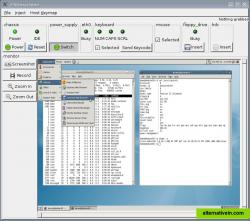
additionally, faumachine can not only simulate a pc, but also its environment, like power switches, the monitor, the power supply and even the interaction of the user. the virtual user can recognize text and bitmaps on the screen and react to it by typing, moving and clicking the mouse, pressing the reset button, and the like.
one of the main differences to other virtual machines like qemu, virtualbox, bochs or vmware is, that faumachine can be configured on a very fine granular level. such details include, to what memory bank a memory module is connected to, or which pcislot a pcicard is inserted into.
of course faumachine supports networking. it can be connected to the local network which its host machine is attached to in a masqueradinglike way using slirp, or even transparently via a tun/tapbridging interface. if the appropriate servers are running on the faumachine, login from any real machine is possible, once the network is set up.
faumachine has the ability to take screenshots of the simulated monitor. it also comes with facilities to record a movie of the virtual screen during simulation, which can be recoded to ogg/theora using our tool faumencoder.
 3 Like
3 Like 2 Like
2 Like 2 Like
2 Like 2 Like
2 Like